In nursing, rehabilitation, and long-term care environments, lift transfer chairs are extremely practical assistive devices. They help caregivers perform transfers in various scenarios, such as moving from a bed to a wheelchair, from a wheelchair to the toilet, or from a chair to a sofa. The lifting mechanism makes the entire transfer process more effortless and safer, reducing the energy expenditure and physical burden on caregivers.
Currently, lift transfer chairs on the market are mainly divided into two categories:
• Hydraulic lift transfer chairs
• Manual lift transfer chairs
Many users are often confused when choosing between these two types: What are the differences in lifting methods? Does it affect safety? Which one is more suitable for their specific use case? In this article, we will delve into these questions and provide a clear comparison to help you make an informed decision.
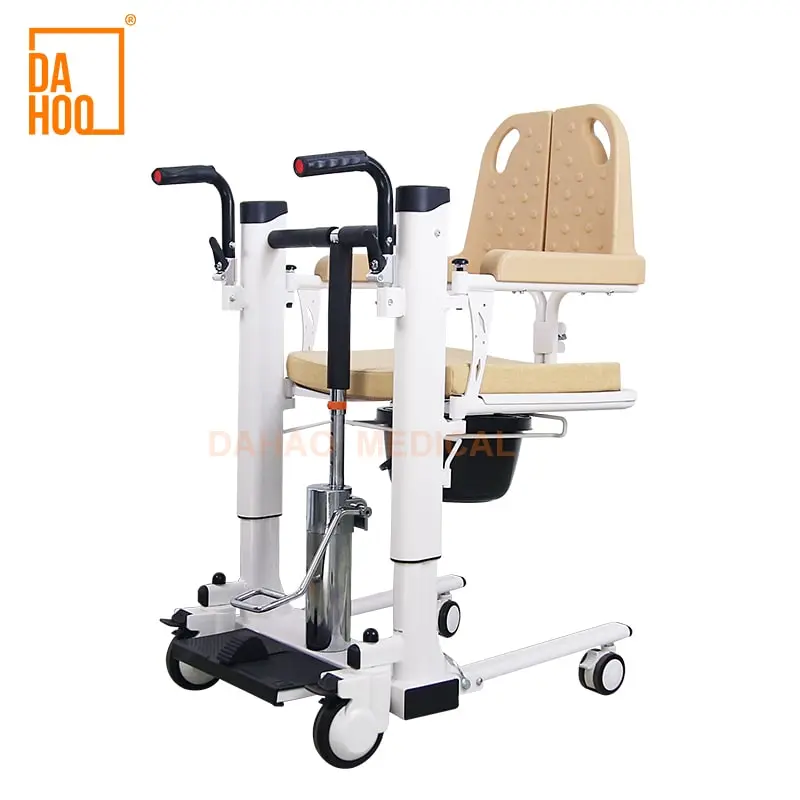
Why is the lifting mechanism the core of a lift transfer chair?
Among all assistive transfer devices, lifting capability is one of the key functions. The reason why lift transfer chairs are safer and more effortless than traditional transfer methods is that they can:
• Smoothly lift the user's body height
• Control the descent speed
• Avoid the risk of falls that may occur during manual lifting
• Allow caregivers to perform transfer movements in a more natural posture
• Reduce strain on the lower back, protecting the caregiver's body
Whether it's a hydraulic or manual lift transfer chair, their core task is to help users maintain stability during the transfer process. However, the difference in lifting methods affects the operating experience, efficiency, care intensity, and the scope of application of the equipment.
What are the structural differences between hydraulic and manual lift transfer chairs?
Structural differences are fundamental to understanding the differences between the two.
1. Structural characteristics of hydraulic lift transfer chairs
Hydraulic lift transfer chairs use a hydraulic cylinder as the power core, achieving lifting and lowering through pressure changes in the hydraulic system.
Typical structure includes:
• Hydraulic cylinder
• Hydraulic pedal or manual hydraulic lever
• Stable support frame
• Adjustable seat or support surface
• Load-bearing support points
The hydraulic system itself can provide high output force, allowing caregivers to complete lifting and lowering with minimal effort.
2. Structural Characteristics of Manual Lift Transfer Chairs
Manual lift transfer chairs typically use mechanical structures for lifting and lowering, such as:
• Cranks
• Hand levers
• Manual levers
• Simple linkage systems
They do not rely on hydraulic or pneumatic power, but instead use human power to drive the mechanical structure to raise or lower the seat.
3. The Core Difference Between the Two Comes from the Power Source
Lifting Mechanism | Power source | Features |
| Hydraulic lift transfer chair | Hydraulic system assisted | Stable, labor-saving, suitable for frequent operation |
| Manual lift transfer chair | Completely human-powered | Operation is more strenuous, but the structure is simpler |
The different structures lead to significant differences in lifting experience, safety, and applicable scope.
Is there a big difference in user experience between the two?
The difference in experience is one of the most important factors for users and a crucial factor in determining whether a lift transfer chair is suitable for a particular care scenario.
1. User Experience of Hydraulic Lift Transfer Chairs
The characteristics of hydraulic systems are:
• Smooth lifting and lowering process
• Stable power output
• Lifting and lowering can be completed with only slight pressure or operation
• Effortless even when transferring heavy users
This means that caregivers experience less physical exertion when using hydraulic lift transfer chairs, especially in:
• Scenarios requiring multiple transfers per day
• Scenarios with heavier users
• Scenarios where the caregiver has limited physical strength
In these scenarios, the advantages of the hydraulic lifting system are very obvious.
2. User Experience of Manual Lift Transfer Chairs
Because they rely entirely on human operation, the experience is usually affected by the following factors:
• The caregiver's arm strength
• The user's weight
• Changes in lifting height
When transferring heavier users, manual lifting may become strenuous, and may even require two people to complete the task.
In general, the difference in experience mainly comes from the smoothness of the lifting process and the amount of force required, and hydraulic lifting is significantly easier and smoother.

Which is more labor-saving: hydraulic or manual lift transfer chairs?
Undoubtedly, hydraulic lift transfer chairs are more labor-saving. The reasons include:
1. Hydraulic systems amplify human power
The hydraulic cylinder structure itself has the characteristic of "efficient power output," allowing for lifting heavier objects with less force.
2. The operation is more ergonomic
For example, lifting and lowering are completed by stepping on a pedal or lightly pushing a hydraulic lever, reducing bending, twisting, and excessive gripping force.
3. User weight has less impact on the force required
Even when transferring heavier users, caregivers do not need to exert excessive force, which is something that manual lifting cannot match. Manual lifting becomes significantly more strenuous as the user's weight increases, making it less convenient for long-term use.
Are there differences in safety between these two types of lift transfer chairs?
Safety is one of the most important factors when choosing a lift transfer chair.
1. Safety Features of Hydraulic Lift Transfer Chairs
Hydraulic lifting typically features:
• Smooth lifting and lowering, avoiding sudden drops
• Controllable lowering speed
• Less prone to sudden movements or jamming
• More consistent center of gravity movement
Therefore, hydraulic lifting provides greater stability when transferring users who are prone to losing their balance.
2. Safety Features of Manual Lift Transfer Chairs
Manual structures are also reliable in terms of safety, but:
• Uneven operating speed may cause "jerky" movements
• Requires the caregiver to maintain stable force during lifting and lowering
• Excessive force on the knees or lower back may affect postural stability
• The heavier the user, the higher the safety risk
While not inherently unsafe, it requires greater skill from the caregiver.
What are the differences in maintenance between the two?
1. Maintenance of Hydraulic Lift Transfer Chairs
Hydraulic equipment requires:
• Regular inspection of hydraulic cylinder seals
• Avoiding hydraulic fluid leaks
• Maintenance of hydraulic pedals or support mechanisms
The hydraulic system is more complex than the mechanical structure, so maintenance requirements are slightly higher.
2. Maintenance of Manual Lift Transfer Chairs
Due to its simple structure, it usually only requires:
• Checking that the hand crank and lever operate smoothly
• Lubricating mechanical contact points
• Ensuring that connecting parts are secure
Therefore, manual lift transfer chairs are more convenient for long-term maintenance, reducing maintenance costs.

Which type of lift transfer chair is suitable for frequent use by caregivers?
If caregivers need to:
• Perform transfers multiple times a day
• Transfer heavy users
• Use the chair frequently in hospitals, nursing homes, or at home
Then a hydraulic lift transfer chair is more suitable.
It significantly reduces:
• Strain on the caregiver's lower back
• Arm strength exertion
• Long-term fatigue
• The risk of instability during operation
Conversely, if the frequency of use is low, or the user's weight is light, a manual lift transfer chair can also meet daily needs.
Which type of lift transfer chair is suitable for users with different weights and physical conditions?
1. Heavy Users
A hydraulic lift transfer chair is more recommended because it reduces the physical burden on caregivers.
2. Caregivers with Limited Strength
Hydraulic lifting is a more effortless and safer option.
3. Users Requiring a Smoother Lifting Process
Hydraulic lifting provides a more stable and smooth experience.
4. Low Frequency, Occasional Use
Manual lifting can meet basic needs, with a simpler structure and lower cost.
How to choose between hydraulic and manual lift transfer chairs when purchasing?
You can consider the following four dimensions:
1. Frequency of Use
High frequency → Hydraulic lifting
Low frequency → Manual lifting
2. User Weight
The heavier the user, the more recommended the hydraulic lift.
3. Caregiver Strength
Limited caregiver strength → Hydraulic lifting
Good caregiver strength → Manual lifting is also acceptable
4. Budget
Manual lifting is generally more economical, while hydraulic lifting offers higher performance but at a higher cost.
Understanding the Differences, Choose the More Suitable Lift Transfer Chair
Although both hydraulic and manual lift transfer chairs belong to the same category, there are significant differences in structure, operation experience, force required, safety performance, and applicable scenarios.
Advantages of hydraulic lift transfer chairs include:
• Smooth lifting
• Effortless operation
• More suitable for heavy users
• More suitable for high-frequency care scenarios
Advantages of manual lift transfer chairs include:
• Simple structure
• Low maintenance costs
• More economical price
• Suitable for lightweight use scenarios
The final choice should be based on:
• User weight
• Caregiver strength
• Frequency of use
• Budget and maintenance capabilities
A comprehensive assessment should be made.
What are the payment and shipping options for bulk orders?
For bulk orders, Dahao Medical offers a range of payment and shipping options to make purchasing as convenient as possible. We accept major payment methods, including bank transfers, PayPal, and credit card payments, ensuring secure transactions. Our shipping options are flexible, with door-to-door delivery available to most countries. We work with reliable logistics partners to ensure your products arrive on time and in perfect condition.


